SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19, Corona 19) virus mutation
According to the classification of the SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group (SIG), the COVID-19 virus mutation consists of three classes and it was named by the WHO in the order in which they were discovered.
COVID-19 virus mutation is caused by substitution or a combination of substitutions in amino acids located at specific sites in the spike protein on the surface of the virus, and there are the following mutations
- L452R
- E484K
- L452R, E484Q
- K417N, E484K, N501Y
- K417T, E484K, N501Y
- K417N, L452R, T478K
- R346K, E484K, N501Y
※Tip: L452R refers to a mutation in which the 452th amino acid L (leucine) of the spike protein on the surface of the virus is substituted with R (arginine).
▶COVID-19 virus mutation classification
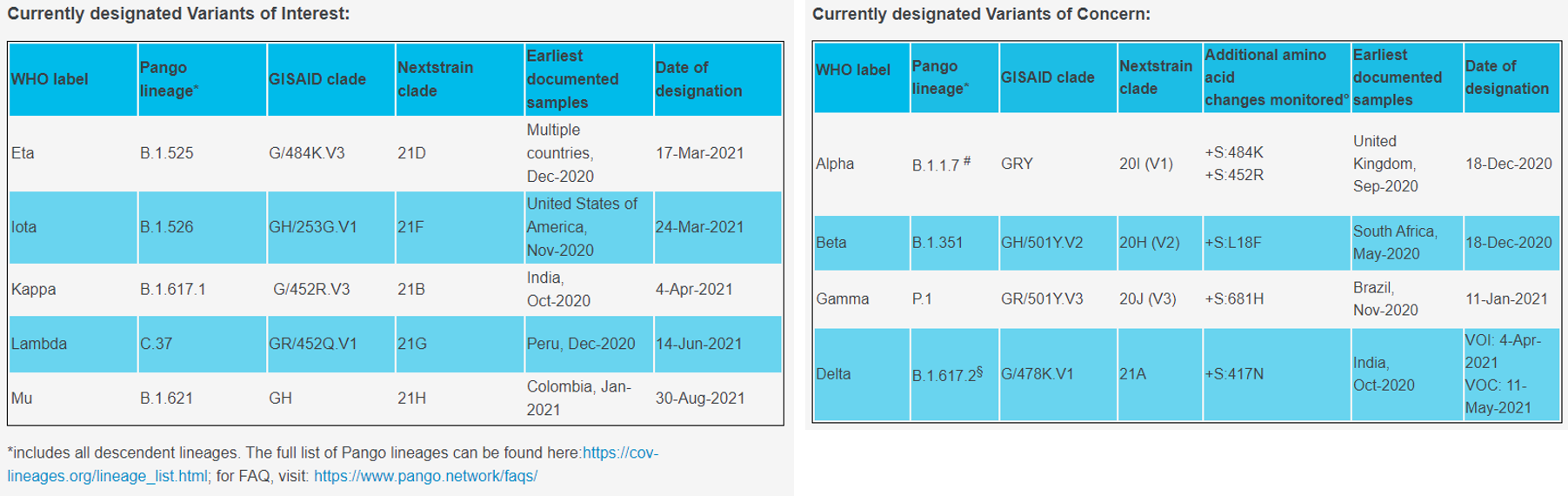
1) Variant of Interest
: Mutations occur in specific genes associated with receptor binding changes, which weaken the neutralizing response of antibodies generated by previous infections or vaccinations, reduce the effectiveness of treatment, affect diagnosis, or predict the severity of infectivity or disease an increase was observed.
① Eta, B.1.525
- First discovered in the UK and Nigeria at December 2020
- Spike protein substitution: A67V, 69del, 70del, 144del, E484K, D614G, Q677H, F888L
- There is a possibility that the neutralization effect may be reduced by the treatment of some emergency use authorization (EUA) monoclonal antibody, and the neutralization effect by the serum after the convalescence period and vaccination may be reduced.
② Iota, B.1.526
- First confirmed in New York, USA at November 2020
- Spike protein substitution: L5F, (D80G*), T95I, (Y144-*), (F157S*), D253G, (L452R*), (S477N*), E484K, D614G, A701V, (T859N*), (D950H *), (Q957R*)
- Decreased sensitivity to bamranivirumab and etecevumab monoclonal antibody treatment combination therapy (however, the clinical significance of this reduction is unknown, but alternative monoclonal antibody therapy is available) and recovery and neutralizing effect by serum after vaccination is decreased.
③ Kappa, B1.617.1
- First confirmed in India at December 2020
- Spike protein substitution: (T95I), G142D, E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, Q1071H
- There is a possibility that the neutralizing effect may be reduced by some EUA monoclonal antibody treatment and there is a possibility that the neutralizing effect by the serum after vaccination may be reduced.
④ B.1.617.3
- First confirmed in India at October 2020
- Spike protein substitution: T19R, G142D, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, D950N
- There is a possibility that the neutralizing effect may be reduced by some EUA monoclonal antibody treatment and there is a possibility that the neutralizing effect by the serum after vaccination may be reduced.
2) Variant of Concern
: There is markedly increased virus transmission, increased severity (increased hospitalization or death), decreased neutralizing effect by antibodies resulting from previous infection or vaccination, decreased efficacy of treatment or vaccine, and evidence of mutation detection failure in diagnostic tests mutation.
① Alpha, B.1.1.7, Q sublineages
- First confirmed in the UK
- Spike protein substitution: 69del, 70del, 144del, (E484K*), (S494P*), N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H (K1191N*)
- ~50% increase in infectivity and potential increase in severity based on hospitalization and mortality, no effect on sensitivity to EUA monoclonal antibody treatment, minimal effect on neutralizing effect by serum after recovery and vaccination.
② Beta, B.1.351, B.1.351.2, B.1.351.3
- First confirmed in South Africa
- Spike protein substitution: D80A, D215G, 241del, 242del, 243del, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G, A701V
- Increased infectivity by ~50% and significantly reduced sensitivity to combination therapy with bamranivirumab and etesevirumab monoclonal antibody treatment, but other EUA monoclonal antibody treatment is possible.
③ Delta, B.1.617.2, AY.1. AY.2, AY.3
- First confirmed in India
- Spike protein substitution: T19R, (V70F*), T95I, G142D, E156-, F157-, R158G, (A222V*), (W258L*), (K417N*), L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N
- Possibility of reducing the neutralizing effect due to increased transmission power and treatment with some EUA monoclonal antibodies, and the possibility of reducing the neutralizing effect by serum after vaccination.
④ Gamma, P.1, P.1.1, P.1.2
- First confirmed in Japan and Brazil
- Spike protein substitution: L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y, T1027I
- Sensitivity to the combination therapy of bamranivirumab and etexevirumab monoclonal antibody treatment is significantly reduced, but other EUA monoclonal antibody treatment is possible, and the neutralizing effect of serum after recovery and vaccination is reduced.
3) High-risk Variants: none identified
※Related documents can be checked on the source site below.
Source: https://korean.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-info.html#Interest



